Initiatives to prevent
global warming
Since its establishment in 1952, the ARE Holdings Group has developed its business activities to protect the global environment with the purpose of being "Totally Committed to Protecting the Natural Environment and Preserving Resources," and with the aim to be a leader in creating a circular economy that connects society to the environment.We are achieving both business growth and the solutions to social issues.
Climate change is a common challenge for humankind, and we believe it is one of our business materiality themes. In order to achieve a sustainable society, we will contribute through business activities and reduce our own CO2 emissions.
Disclosures Based on Recommendations of the Task Force on Climate-Related Financial Disclosures (TCFD)
Expressed to Endorse the TCFD and Strengthening the Governance System
In December 2021, we expressed our endorsement for the recommendations of the Task Force on Climate-Related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) and established a cross-company team for TCFD consisting of Business Unit, Technical Unit, and Administration Unit in order to identify risks and opportunities related to climate change and understand the medium- to long-term impact of climate change on our business, and have considered the countermeasures.
Furthermore, to strengthen the sustainability promotion system, the previous SDGs Promotion Committee has been expanded and will be supervised by the representative director, Representative Director, President & CEO president, changing to a Sustainability Committee consisting of directors in charge of the Business Unit, Technical Unit, and Administration Unit (April, 2022). The Sustainability Committee deliberates on sustainability strategies, plans, policies, risk management, and monitoring on a quarterly basis. Important matters will also be reported at the Group Executive Committee. Climate change-related issues have been addressed in the SDGs Promotion Team, but will be addressed in the Climate Change Working Group.
The Board of Directors shall be informed of the matters discussed by the Sustainability Committee, and important matters shall be resolvedby the Board of Directors to ensure effective governance.
The risks and opportunities identified in the TCFD actions will be reported to the Board of Directors and the Sustainability Committee at least once every year.

Strategy
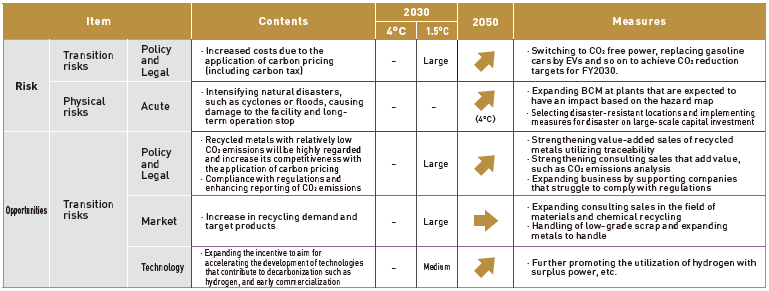
Extraction of Risks and Opportunities
We extracted risks and opportunities relevant to climate change that will affect our precious metals business (domestic and North American businesses) and environmental preservation business in 2030. We qualitatively assessed them on three levels: "Large", "Medium", and "Small". At that time, we also considered the further impact of climate change from 2030 toward 2050. As a result, "Policy and Legal," "Market," "Technology," etc. were identified.
Summary of Scenario
In the next place, we conducted a scenario analysis to investigate the impact on the business. We adopted two scenarios. One is that the global average temperature is expected to increase by around 4°C by 2100, and the other is that the global average temperature is expected to increase by 1.5°C by 2100, compared to that before the industrial revolution. The analysis was based on the World Energy Outlook 2021 by the International Energy Agency (IEA), the reports by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), and other materials published by the Japanese government.
Results of Scenario Analysis
The 4°C scenario is a world where the current situation continues on, and we found that there would be little impact as of 2030. On the other hand, as we move toward 2050, we anticipate an increase in physical risk: the intensification of natural disasters such as cyclones or floods caused by abnormal weather.
In addition to formulating business continuity management (BCM), we are also taking actions such as selecting a location that is strong against disasters when a plant is moved.
In the 1.5°C scenario, strong policy measures are expected to be taken to achieve carbon neutrality in the mid-century. One of these risks is the introduction of carbon pricing including carbon tax. Being affected by cost increases will become a risk, especially in the environmental preservation business. On the other hand, in the precious metals business, it is likely that the evaluation of recycled metals with relatively low CO2 emissions and their cost superiority will increase. This is an opportunity for the company, which has strengths in the production and traceability of recycled precious metals. In the environmental preservation business, the shift from simple incineration to thermal recycling during the transition to decarbonization will be an opportunity for our company which has already been addressed. The expansion of recycling demand, including the expansion of the target product, will provide an opportunity to take advantage of our strength in consulting sales (proposal-based sales).
While reducing risk, we will focus on expanding opportunities.
Risk Management
The Climate Change Working Group will compile the status of responses to risks and opportunities related to climate change and CO2 emissions. The Sustainability Committee will monitor and evaluate them each year. The Board of Directors will also be informed of the contents for supervision and direction. Also, by reporting it to the Group Risk Management Department, it will be reflected in the overall group risk management.
Metrics and Targets
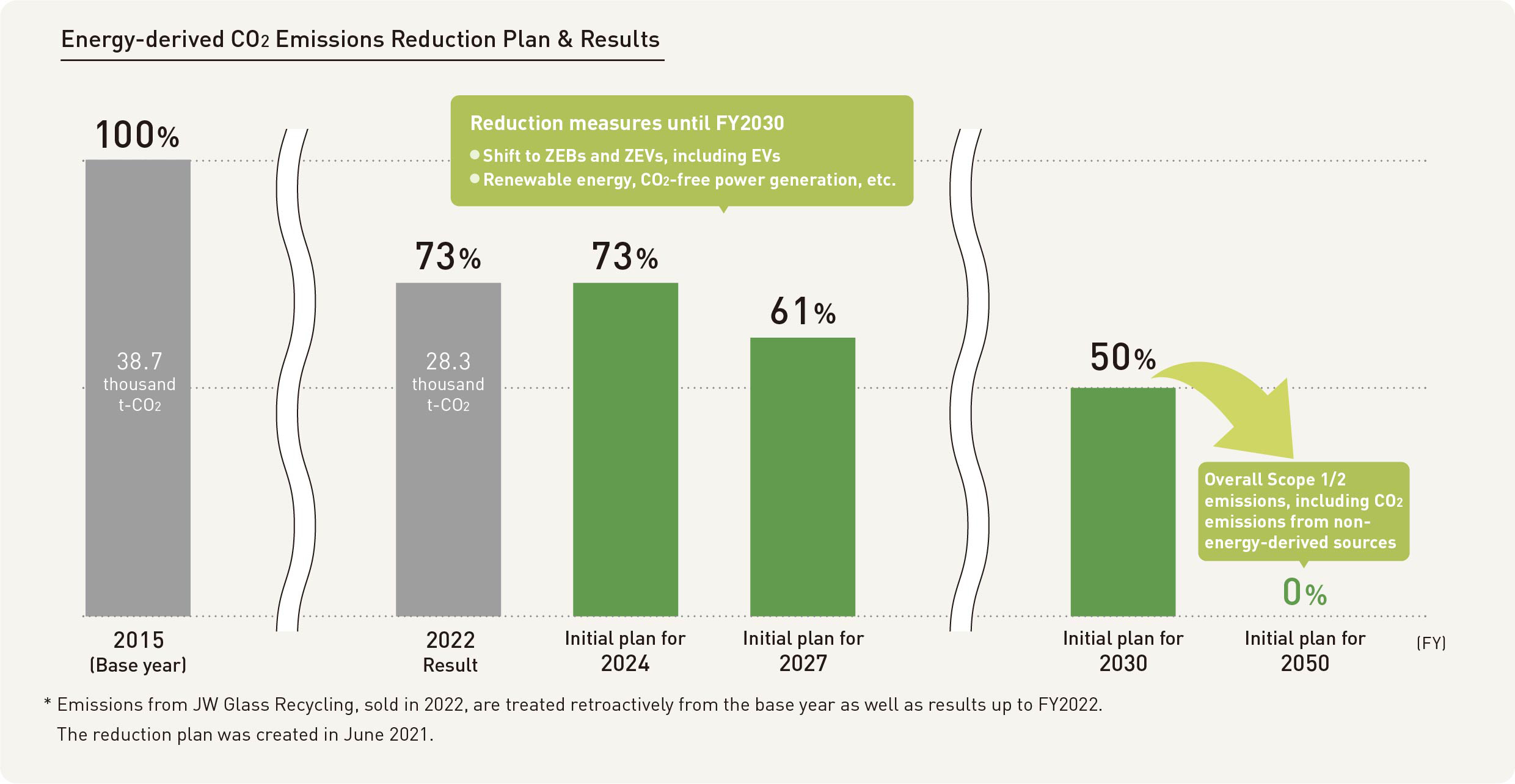
One of our business materiality themes is to reduce CO2 emissions. Accordingly, we have set the following targets:
● Reduce CO2 emissions from energy sources, such as electricity and gasoline, by 50% (compared to FY2015) by FY2030
In order to achieve the target, we are moving forward with switching to CO2 free electricity, reducing fuel usage, and making our business offices ZEBs (Zero Energy Buildings). We have also declared that we will aim to become carbon neutral in FY2050 (targets are Scope 1 and Scope 2).
Although we recycle industrial waste that can be recycled in our environmental preservation business, it is also true that there are some things that must be incinerated to ensure proper disposal, such as reduction and detoxification. Therefore, we will first focus on achieving our energy-derived CO2 reduction target.

CO2 emission trends
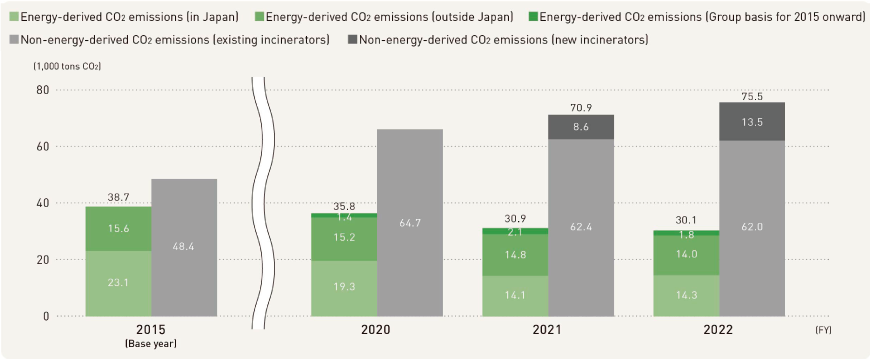
In FY2021, the Group's total CO2 emissions were up approximately 4% from FY2015. This does not include the emissions attributed to one site in Japan and one outside Japan that joined the Group after the base year. Energy-derived CO2 emissions remained at about the same level overseas, but in Japan, they were reduced due to consumption of high-efficiency selfgenerated power using waste to energy facility as well as a review of each site's electricity contract plans. The result was an overall reduction of 27%. On the other hand, non-energy-derived CO2 emissions generated through industrial waste incineration were up approximately 29% from FY2015, but the lifespan of final disposal sites was extended by incinerating waste plastic and drastically reducing its volume.
If we look at the CO2 emissions above by Scope, Scope 1 emissions account for 89,600 tons of CO2, and Scope 2 emissions account for 13,400 tons of CO2. Scope 3 emissions account for 137,200 tons of CO2.
<Scope of data>
Headquarters, sites, sales offices and plants in Japan, as well as Group companies* and overseas subsidiaries* (calculation period: April to March)
*The data pertains to consolidated subsidiaries as of March 31, 2022. Data for deconsolidated subsidiaries has been subtracted retroactively, while data for subsidiaries that were previously non-consolidated has been added retroactively, going back to the fiscal year when the subsidiary became consolidated.
<Calculation method>
Energy-derived emissions: Calculated based on the amounts of electricity and fuel consumed at each site (emissions in Japan calculated based on the Act on Promotion of Global Warming Countermeasures and the Act on the Rational Use of Energy)
Non-energy-derived emissions: Calculated based on the amount of industrial waste incineration.
2050 Carbon Neutrality Declaration
We have declared that as another long-term goal, we aim to achieve carbon neutrality in FY2050 in Scope 1 (direct emissions from the company itself) and Scope 2 (indirect emissions due to energy used that was supplied by others). We also aim to disclose values and develop a long-term reduction plan for Scope 3 (indirect emissions aside from Scope 1 and 2, and emissions from others that are related to the company's activities).